现有一棵无向、无根的树,树中有 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n - 1 编号。给你一个整数 n 和一个长度为 n - 1 的二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。
每个节点都关联一个价格。给你一个整数数组 price ,其中 price[i] 是第 i 个节点的价格。
给定路径的 价格总和 是该路径上所有节点的价格之和。
另给你一个二维整数数组 trips ,其中 trips[i] = [starti, endi] 表示您从节点 starti 开始第 i 次旅行,并通过任何你喜欢的路径前往节点 endi 。
在执行第一次旅行之前,你可以选择一些 非相邻节点 并将价格减半。
返回执行所有旅行的最小价格总和。
示例 1:
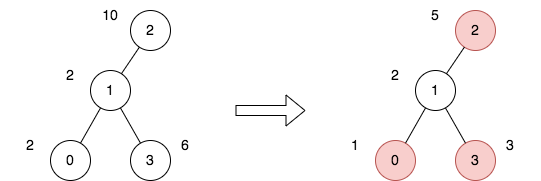
1 | 输入:n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,3]], price = [2,2,10,6], trips = [[0,3],[2,1],[2,3]] |
示例 2:
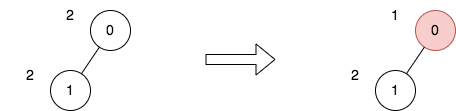
1 | 输入:n = 2, edges = [[0,1]], price = [2,2], trips = [[0,0]] |
根据最短路径构造一颗新树,然后用树上 DP 求非相邻节点的最大路径和,将这条路径和减半即可得到最终答案:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41class Solution:
def minimumTotalPrice(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]], price: List[int], trips: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append((b, price[b]))
g[b].append((a, price[a]))
def dijkstra_path(start, end): # 存储最短路径
dist = [float('inf')] * n
dist[start] = 0
heap = [(0, start, [])]
while heap:
d, u, path = heapq.heappop(heap)
if u == end:
return path + [u]
if d > dist[u]:
continue
for v, w in g[u]:
if dist[u] + w < dist[v]:
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
heapq.heappush(heap, (dist[v], v, path + [u]))
return []
price_n = [0] * n
for s, e in trips:
path = dijkstra_path(s, e)
for node in path:
price_n[node] += price[node]
dp = [[0] * 2 for _ in range(51)]
for i in range(n):
dp[i][1] = price_n[i]
def dfs(x, f):
for y, _ in g[x]:
if y != f:
dfs(y, x)
dp[x][1] += dp[y][0]
dp[x][0] += max(dp[y][1], dp[y][0])
dfs(0, -1)
return sum(price_n) - max(dp[0][0], dp[0][1]) // 2